Importance of kidney
Kidney forms a vital organ of your urinary tract. In humans we have two kidneys located on two sides of the spine. Its job is to filter wastes from the blood and also to remove extra fluids as urine.
By removing toxins, acids, other wastes as well as extra fluids from the body, the kidney keeps a proper balance of various minerals of the blood such as potassium, sodium, calcium and phosphorus.
But for these vital functions of the kidney it is impossible for the various tissues of the body including muscles, nerves etc to work synergically.
Kidney diseases
Due to various reasons kidney damages occur when the kidney fails to function properly. The reasons for kidney damage can be diabetes, high blood pressure and some other chronic conditions affecting the patient for a longer time.
During the initial stages of kidney damage, it does not manifest noticeable symptoms. Gradually the disease takes hold causing the stoppage of kidney functions.
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic Kidney Disease or CKD is the most commonly found disease of the kidney. It is mainly caused due to prolonged high blood pressure.
High blood pressure slowly damages the Glomeruli, which are tiny blood vessels responsible for filtering the wastes from the blood. As the condition persists further damages occur to the Glomeruli. The functioning of the kidney is greatly affected.
Diabetes is another major cause of kidney diseases. The increased levels of sugar in the blood also damages the tiny blood vessels of the kidney. This also may lead to kidney failure.
Finally the kidney will stop functioning causing various debilitating conditions.
Treatments of CKD
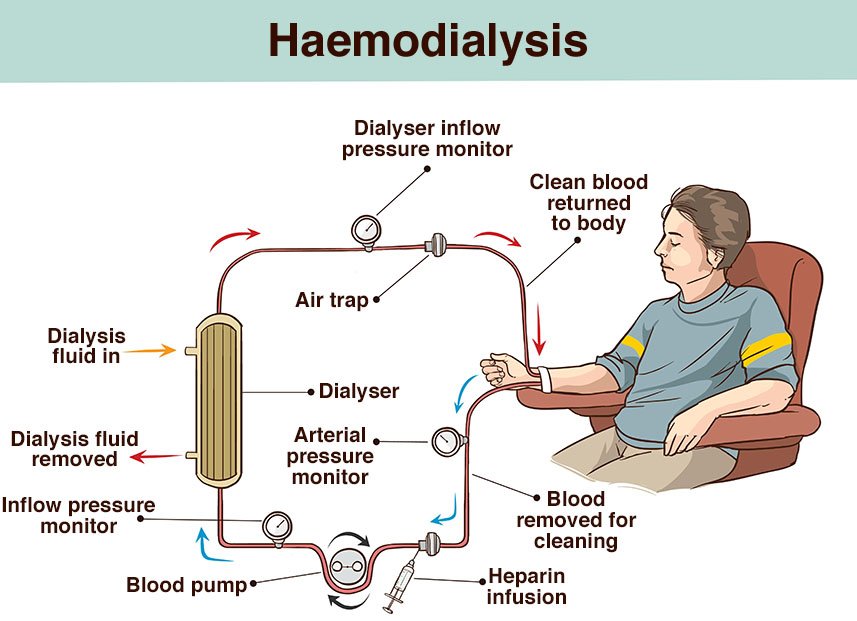
The immediate remedial treatment at such conditions is dialysis. In such treatment the patient has to get admitted to hospital at regular intervals. External machines will help in filtering the blood from wastes and extra fluids in lieu of the kidney.
Dialysis is one kind of stop gap arrangement and cannot cure CKD.
The next option available is kidney transplant.
In this treatment the patient has to undergo surgery. The failed kidney is replaced by a donated kidney. But not all people with CKD are eligible for kidney transplant.
Generally one kidney is replaced in kidney transplant. In spite of the fact that we have two kidneys, a person can survive with a single kidney only.
In this treatment option the patient can avoid the need of frequent dialysis. It gives a longer and more active life to the patient.
One negative point of kidney transplant is the body’s autoimmune attack on the new kidney. For this the patient has to take immunosuppressant medicine. Due to this the patient remains prone to infections and has to be very careful.
Before the kidney transplant the patient has to undergo tests to verify whether the blood of the donor and receiver is matching. Only when the test would show that there is no antibody reaction, the further transplant procedure can follow.
Kidney stones
Sometimes stones are formed in the kidney obstructing the flow of urine. This can be very painful but can be treated easily with the help of modern tools. Sometimes the stone comes out of its own through the kidney.
Glomerulonephritis
In this disease the tiny blood vessels of the kidney known as Glomeruli are infected. It often is cured of its own.
Urinary tract infection ( UTI )
It occurs due to bacterial infection on any part of the urinary system. This disease can be easily treated with medicine. But it should not be left uncared as it may lead to kidney failure when untreated.
Symptoms of kidney diseases
The early warning symptoms of kidney disease are
- Swollen feet and ankles
- Fatigue
- Sleeping problem
- Lack of appetite
- Increased frequency of urination
- Muscle cramping
The symptoms of CKD
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Anemia
- Signs of fluid retention
- Raised levels of potassium
- Changes in the output of urine
Latest scientific approach to treat CKD
The latest approach of modern science towards treating CKD is being envisaged by collaborating with the knowledge of data processing.
Genetic datasets are being prepared from actual patients and the dataset is used in various statistical modeling techniques to estimate the effects of various predictable options.
The latest approach is to deal at the molecular level and suggest targeted treatments with the help of different biomarkers.
Data banks are available which have genome-wide-expression-profiles-samples which have been developed taking data from all stages of CKD of real patients.
The research team is using other latest techniques like machine learning as well as artificial intelligence for classification of the patients into homogenous-subclases.
The aim is to find various urinary biomarkers which can be used to classify the CKD patients. With this latest approach it will be possible to suggest tailored treatment options for individual patients.
CKD is one type of kidney disease which can be due to many reasons. Most of the mechanisms of the kidney which are underlying in the system are still unknown to the medical community.
In this backdrop use of Exome Sequencing is being looked upon as a powerful tool in the treatment of CKD. We can use the analytical and diagnostic-techniques of the Exome Sequencing to understand CKD in a better way.
CKD is unique because of its many causal reasons as well as offering similar symptoms. Hence a molecular approach to the treatment is quite a logical step. In this approach we may hope to find some patient-specific and effective treatment options in the near future.
One study has been done on 3300 patients using exome sequencing. The result of the study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
It could identify causative genetic variants that could be potential causative factors for the CKD in 9% of patients. Another significant revelation of the study was that six genes together accounted for 2/3rd of genetic diagnoses.
Such analysis significantly enhances our understanding of the diseases. Possibilities are bright that by early genetic diagnostic testing we will be able to identify and extend patient-specific therapies.
3D bioprinting
Such latest ground-breaking techniques have made it possible to test compound-behavior. In the near future it is hoped that it will be possible for us to shed fresh light on disease mechanisms which were quite elusive previously.
3D bioprinting simulates techniques similar to printing using fugitive ‘ink’. By printing on to gelatin/fibrogen matrix it is possible to pattern tubular as well as vascular channels.
3D modeling has already been bioprinted using kidney blood vessels and tubules. Further progress is required to replicate the kidney functions making it relevant as well as a realistic system model.
In the distant future it might be possible to even create a synthetic kidney. Understanding all the kidney dysfunctions applying 3D bioprinting is the preceding development to this novel aim.
Organs-on -chips technology
This is the latest technique and uses a microengineered system model. Using this technique attempts are being made to model Glomerulus.
In CKD patients the Glomerulus which are the tiny blood vessels engaged in filtering the blood, gets damaged. The exact reason for the breakdown of the Glomerulus is still unknown to medical science.
Kidney is composed of 20 varying cell types. The normal functioning of these cell types depend on crosstalk among the cell types as well as their interaction with the micro-environment.
By employing Organ-on-chip techniques it is possible to simulate the environment of a real kidney. The flow of the model closely represents blood flow transporting the nutrients, disposing the waste of the blood as well as stimulating the mechanical force.
In this way it is possible to co-culture different cell-types. Interaction between cell types as well as various signals can be examined both for the healthy kidneys as well as for the diseased ones.
By using organ-on-chip techniques it is possible to add conditions such as flow and shear stress creating a situation quite similar to the real kidney. We will be able to collect more and more information.
Our ultimate aim is to treat the conditions after inducing them.
Cell therapy
With the accumulation of more and more knowledge regarding the cells which are found to be involved in the occurrence of CKD, the next stage of treatment is set to be the invention of most useful therapeutic targets.
The latest research in this field is targeting to explore the usefulness of one type of stem cell called “renal progenitor cell”. The idea is to replace the damaged kidney cells with progenitor cells.
The stem cell can be given either intravenous channel or directly to the kidney itself. The beauty of the stem cell is that it will identify the damaged cells and replace those cells which are broken down due to the CKD.
With the application of the latest cellular models it is now possible to exactly mimic the kidney functioning giving us a new tool for various therapeutic alternatives.
Kidney organoids will be used as a new therapy. The future plan is to implant such kidney organoids into the kidney which will help the kidney to repair as well as boost kidney functions.
Cell therapy has attracted the attention of the modern scientific community. The potential application of cell therapy can extend to replacing the non functioning heart muscles and restore heart health.
In the case of organ transplant, the body’s auto-immune system tends to attack the new organ. In such situations cell therapy can be profitably used.
Probably it will be possible to bring a balance among the immune cells with an aim so that the immune system no longer attacks our healthy tissues.
In the very distant future it may even be possible to grow kidney organoids. This will surely revolutionize the treatment approach to CKD. New hopes are seen in the horizons for the unfortunate suffering patients with CKD.
If it is possible to stop further deterioration of the kidney or reverse the progression of the CKD among mid stage to
Organoid
Organoids are tissue cultures which are created from stem cells. Though these are tiny tissue cultures but are self-organized. As the organoids are grown out of stem cells, it is possible for them to replicate the cells of any organ.
With the rapid progress of medical science, it has become almost a reality to grow organoids. Obviously the ability to grow organoids will find many new uses in various medical therapies.
The beauty of the organoids is that it can produce various cells by dividing indefinitely. The scientific community has already been able to create the necessary environment so that the stem cell can carry out the genetic instructions.
The organoids by self organizing can form various cell types as if they are a mini-organ. The size of an organoid can be smaller than a hair to 5 millimeters.
In the near future we will be able to explore all the potential possibilities of mimicking all the organs as well as tissues which are there in our body.
As of now the researchers have already been able to create organoids resembling the organs like kidney, brain, lung, stomach, liver as well as intestine.
By delving deep into tissue culture the scientists will get further insight into the way how the human organs come into existence and grow.
By getting to know more and more information it will be possible to know the exact ways the drugs interact with the organoids. This will eventually lead us to a situation when a revolutionary approach of personalized medicine will be a reality.
This will also open the path towards discovering new kinds of drugs.
Till now the scientific community tried to understand the embryonic development of humans through the animal models and then trying to extrapolate the information on the humans.
With the advent of organoids it is possible now to do human tissue culture directly. It will also open a novel pathway for finding treatment options for many neuropsychiatric diseases such as schizophrenia, autism etc. Such diseases by which a section of the human population are affected, affect the human genome as a whole.